
Overclocking is the process of running hardware at speeds faster than the manufacturer’s intended specs. Overclocking can increase a computer’s speed while compromising stability and thermal performance when done appropriately. Overclocking your GPU and CPU can result in better FPS in games and faster completion of activities like rendering or video editing.
Overclocking your GPU or CPU can deliver a significant speed advantage, but it has certain drawbacks, like higher temperatures and potentially shorter device lifespans. If you’ve tried overclocking and faced problems such as system crashes or excessive heat, you should know how to turn it off.
Modern CPUs have base and turbo clock speeds, allowing the processor to vary its frequency based on the processing demands of the task. Overclocking the CPU involves increasing the base clock while removing the turbo boost, which causes the CPU to run at a faster clock speed.
In this article, we’ll look into overclocking, how to turn it off for the CPU, and answer some frequently-asked questions about it.
- Is Overclocking Safe?
- How do you detect overclocking?
- Making Use of Monitoring Software:
- Clock Speeds:
- Analyze the Results:
- Use the tools and Compare the Outcomes:
- Verifying Factory Overclocking:
- Benefits and risks of overclocking:
- Advantages:
- Disadvantages:
- How to stop overclocking?
- Method 1: Turn off overclocking from windows
- Method 2: Turn off overclocking in the BIOS or UEFI settings
- Accessing the BIOS/UEFI:
- Exit and Save:
- Examine Stability:
- Remove Overclocking Software:
- Conclusion:
- Frequently Asked Questions
Is Overclocking Safe?
Overclocking is a frequently debated topic among PC enthusiasts and gamers. While some enthusiasts actively seek out components with overclocking potential, others are wary due to the inherent risks, especially when overclocking the CPU. Overclocking has the primary benefit of increasing the speed of a processor, which can improve performance for various tasks such as gaming and content creation.
During my testing I observed that one of the primary issues with overclocking is the increased power consumption and heat buildup. Overclocked CPUs require more power, resulting in greater temperatures. This extra heat might cause irreparable damage to your CPU if your PC lacks suitable cooling measures. Furthermore, running a CPU at high clock speeds for lengthy periods might be harmful, resulting in crashes or faults.
To overclock securely, you must take care and be well-informed:
- Invest in cooling systems to efficiently manage the rising heat.
- Make sure your PC case has adequate airflow to dissipate heat.
- While overclocking, keep an eye on temperature and system stability.
- Overclocking should be approached methodically, gradually increasing clock speeds and voltage while testing for stability.
- Conduct an extensive study on your CPU model and motherboard to learn about its overclocking potential and limits.
- Recognize that overclocking may void your CPU’s manufacturer warranty.

How do you detect overclocking?
To detect if your PC is overclocked, use the following software tools and benchmarking techniques:
Making Use of Monitoring Software:
Install one or more monitoring tools on your PC: CPU-Z, GPU-Z, or HWMonitor. These utilities offer data on CPU and GPU frequencies, temps, voltages, and other factors.
Clock Speeds:
Examine your CPU and GPU’s reported clock speeds (frequencies) in the monitoring tool. Compare these clock speeds to the base clock and boost clock values for your components, frequently located in the manual or on the manufacturer’s website.
Analyze the Results:
If the clock speed recorded by the monitoring program exceeds the base clock or boost clock values by more than 5-10%, your PC is probably overclocked. Be aware that some components, such as Intel’s Turbo Boost or AMD’s Precision Boost, have dynamic boost features that can momentarily increase clock speeds beyond the boost clock value under specific conditions.
Use the tools and Compare the Outcomes:
Use a benchmarking tool like Cinebench or 3DMark to evaluate your PC’s performance. Compare your benchmark results to those of other computers with comparable hardware requirements. Benchmark results for various hardware setups are frequently available online. Overclocking may be indicated if your PC’s scores dramatically exceed those of similar systems with the same hardware.
Verifying Factory Overclocking:
Check the specifications for your component on the manufacturer’s or vendor’s website to see whether it has a factory overclock. Some features, such as graphics cards, may have an OC (over-clocked) or SC (super-clocked) suffix in their name, signifying a factory overclock.
By following these procedures, you may determine whether your computer is overclocked. It’s vital to distinguish between manual overclocking, in which users deliberately boost clock speeds, and factory overclocking, in which components are pre-configured with higher clock rates. Understanding the configuration of your system will enable you to make informed judgments about overclocking or restoring to default settings.
Benefits and risks of overclocking:
Overclocking has various advantages but also has hazards and restrictions that users should be aware of before attempting it. Here’s a breakdown of the benefits and drawbacks:
Advantages:
- Overclocking allows you to buy less expensive components and boost their performance to meet or exceed that of more expensive counterparts. Overclocking a mid-range CPU can make it perform similarly to a high-end one.
- It allows you to investigate the performance boundaries of various brands or models of components. Overclocking different GPUs, CPUs, or other hardware will enable you to compare their capabilities under duress and determine which performs better.
- Overclocking can revitalize older devices, bringing them up to speed with modern system requirements. This can help you develop the usefulness of aging hardware without requiring a complete upgrade.
- Surprisingly, some overclocking programs allow you to reduce voltage while boosting clock speed, improving power economy and battery life on portable devices.
Disadvantages:
- Overclocking frequently voids manufacturer warranties. Manufacturers design their components to perform consistently at their default clock rates, and changing these settings may result in the loss of warranty coverage.
- It increases power consumption and heat generation, leading to overheating, melting, or even component failure. Effective cooling solutions, such as additional fans or liquid cooling systems, are frequently required to avoid these dangers.
- It upsets the delicate balance of your system’s components, resulting in instability, crashes, errors, and system freezes. Achieving the ideal blend of performance and stability necessitates extensive testing and tuning.
- The increased stress exerted by overclocking might reduce the lifespan of your components. Overclocked components are more likely to wear out faster than those running at their default speeds, necessitating replacement sooner.
How to stop overclocking?
To prevent overclocking your CPU, return the CPU’s settings to their default values. Here’s a general guide on how to stop CPU overclocking:
Method 1: Turn off overclocking from windows
You can turn off CPU overclocking on Windows 10 by adjusting the power settings. Here’s a step-by-step procedure:
- In Windows, go to the “Settings” menu. Select “System” and “Power & Sleep.”

- On the right, there’s a button, “Additional power settings.” Click on it.

- Make sure the “High performance” option is selected in the “Preferred Plans” section. Then, to the right of it, click the “Change plan settings” button.

- Now, at the bottom of the window, click the “Change advanced power settings” button.

- Locate and expand the “Processor power management” option in the list of advanced power settings.
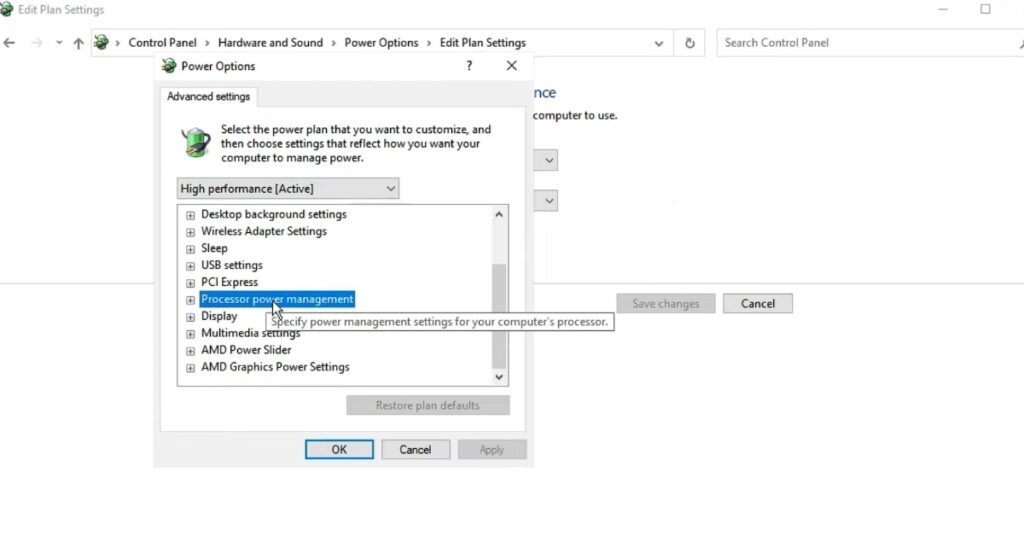
- In the menu, expand the options for “Minimum processor state” and “Maximum processor state.”
- Change the settings for “Minimum processor state” and “Maximum processor state” from 100% to 99%.
- After these changes, click “Apply” then “OK” to save the settings.
These instructions will effectively turn off CPU overclocking on your Windows 10 PC.
Method 2: Turn off overclocking in the BIOS or UEFI settings
Begin by restarting your computer. To stop overclocking your CPU using the BIOS or UEFI settings, you must reverse the adjustments made to your CPU’s clock speed and other associated parameters.
Accessing the BIOS/UEFI:
You’ll need to hit a specific key to reach the BIOS or UEFI menu during the startup process. Typically, this is accomplished by pressing a particular key (such as F2, Delete, F12, or Esc) as soon as your computer loads up. The key to enter this menu differs depending on your computer’s manufacturer. Look for an on-screen notice that says, “Press the key to enter startup,” and follow the instructions. Be careful that this notice is frequently presented for only a few seconds, so you must respond immediately.
Navigate to the area relating to overclocking or performance adjustments once in the BIOS/UEFI interface. This area is commonly referred to as “Advanced,” “Overclocking,” or “AI Tweaker,” however, the name may vary depending on your motherboard.
To access the computer’s UEFI firmware, open the “Settings” menu in Windows. Go to “Update & Security” > “Recovery.” Under “Advanced startup,” click “Restart now.” Windows will restart, and you will see a menu. Navigate to “Troubleshoot” > “Advanced Options” > “UEFI Firmware Settings.” This will send you to the UEFI settings. Search for “Load Optimized Defaults,” “Load Defaults,” or “Reset to Default.”
Exit and Save:
Once the default settings have been loaded, save the changes. This usually entails verifying and quitting the BIOS/UEFI settings by hitting a key (e.g., F10) or browsing to a menu choice that allows you to save changes. This option is usually in a menu labeled “Exit” or “Save & Exit.” Save your changes and restart your computer by following the on-screen directions.
Examine Stability:
After restarting, your computer should be functioning at its default CPU settings. To maintain stability, monitor your system’s performance and ensure it runs smoothly. Run stress tests or benchmarks to ensure that the CPU is working correctly. Your computer will restart with the CPU working at its default settings, prohibiting overclocking. This returns all overclocking settings to their default defaults.
Remove Overclocking Software:
Uninstall any overclocking software installed in your operating system to prevent additional attempts to overclock your CPU.
Conclusion:
Overclocking can improve performance but should be undertaken with caution. The danger of damage and reduced CPU lifespan remains, especially without sufficient cooling. If you’re uncomfortable with the risks or lack the requisite information, avoid overclocking and stay with your CPU’s original settings. So, before attempting to overclock, assess the benefits against the potential negatives and verify you have the requisite knowledge and cooling solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Chrome does not overclock your CPU; it is a web browser that works on your computer’s hardware. Here are some actions to take to address excessive CPU utilization in Chrome:
1. Make sure you’re running the most recent version of Chrome. Arrangements that are too old may have performance concerns.
2. Some Chrome extensions might consume a lot of resources. In the bar, type chrome://extensions/ and disable or uninstall any attachments you don’t require or believe are causing high CPU utilization.
3. Some users have observed improved performance when hardware acceleration is turned off. To do so, navigate to chrome://settings/ and select “Advanced” at the bottom. Disable “Use hardware acceleration when available” under “System,” then restart Chrome.
4. Excessive open tabs in Chrome can deplete CPU and memory resources. Close any tabs that you aren’t actively utilizing to lessen CPU stress.
5. Malware can cause excessive CPU utilization. Run a trustworthy antivirus or anti-malware scan to check for infections on your machine.
6. Ensure that your graphics drivers are up to date, as obsolete or corrupt drivers can impact browser performance.
7. Whether you continue to have excessive CPU utilization with Chrome, you should experiment with alternative web browsers like Firefox, Edge, and Brave to determine whether the problem persists.
How to stop overclocking CPU AMD?
Access your computer’s BIOS/UEFI settings, go to the overclocking or performance sections, and reset all settings to default or load-optimized defaults to cease overclocking an AMD CPU. To reset the CPU’s default clock speeds, save the settings and leave the BIOS/UEFI.
How to stop overclocking CPU Windows 11?
There are a couple of techniques to stop overclocking your CPU using Windows 11. The first option is to turn off overclocking in the BIOS. To do so, restart your computer and navigate to the BIOS menu. This menu is typically opened during startup by pressing a key such as F2 or DEL. When in the BIOS menu, look for a setting like “CPU Overclock.” Once you’ve located it, use the arrow keys to travel to it and turn it off. Save your modifications and exit the BIOS menu.
Another option for stopping CPU overclocking is to utilize a software program such as AMD Overdrive or Intel Extreme Tuning Utility, depending on your platform. You may use these programs to overclock your CPU from within Windows 11. To turn off overclocking, launch the program and go to the “CPU” or “Clock Speed” tab. You should be able to prevent overclocking or return the clock speed to its default value from here. Save your modifications and leave the program. Your CPU should now be operating at its average clock speed.









